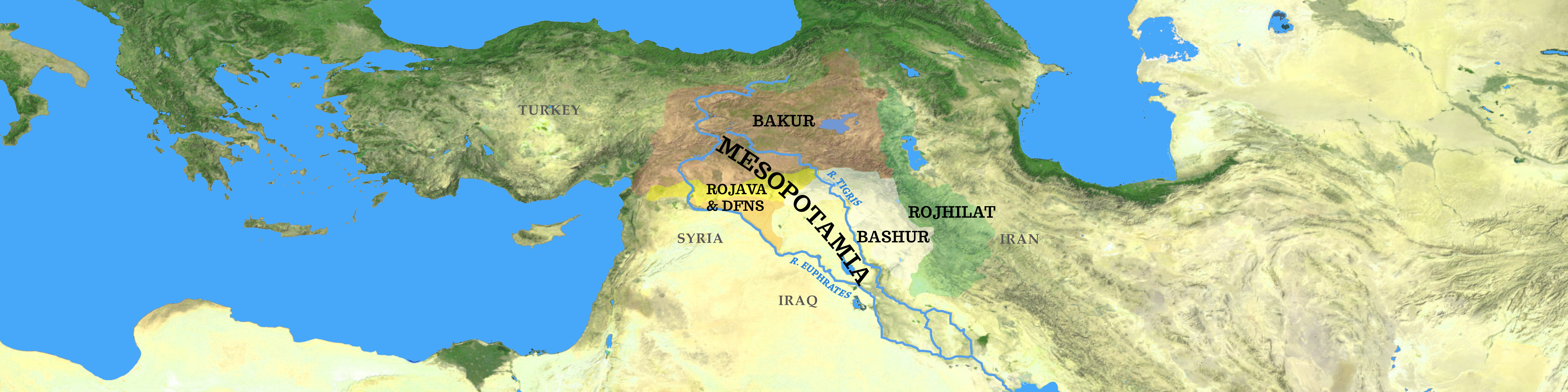
Mesopotamia – the land ‘between two rivers,’ the Tigris and Euphrates – is also known as the cradle of civilisation. It’s a historical region that spanned the land now divided by the nation states of Syria, Iraq and parts of Turkey, Iran, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. It’s an approximate region, without borders. The same could be said of Kurdistan – ‘the land where Kurds live’ – another geographical region which has never been a country, whose people have been divided by some of those same nation states.
Unlike the term ‘Kurdistan’, ‘Mesopotamia’ is not bonded to any national identity, and its use reflects the spirit of pluralism that has emerged from the Kurdish freedom movement. Mesopotamia has always been highly ethnically and culturally diverse.
Co-operation in Mesopotamia researches and raises awareness about the developing co-operative economy in the Democratic Federation of Northern Syria, often referred to as Rojava (Kurdish for ‘West’), and also in Bakur (Kurdish for ‘North’), in southeastern Turkey.